Do your eyes itch frequently or do you experience frequent headaches?This may be your body's way of telling you that you are deficient in magnesium.|Health
Magnesium Deficiency: 5 Silent Symptoms Like Eye Rolls You Should Never Ignore
Do your eyes often tear or do you often get headaches?This may be your body's way of telling you that you are deficient in magnesium.
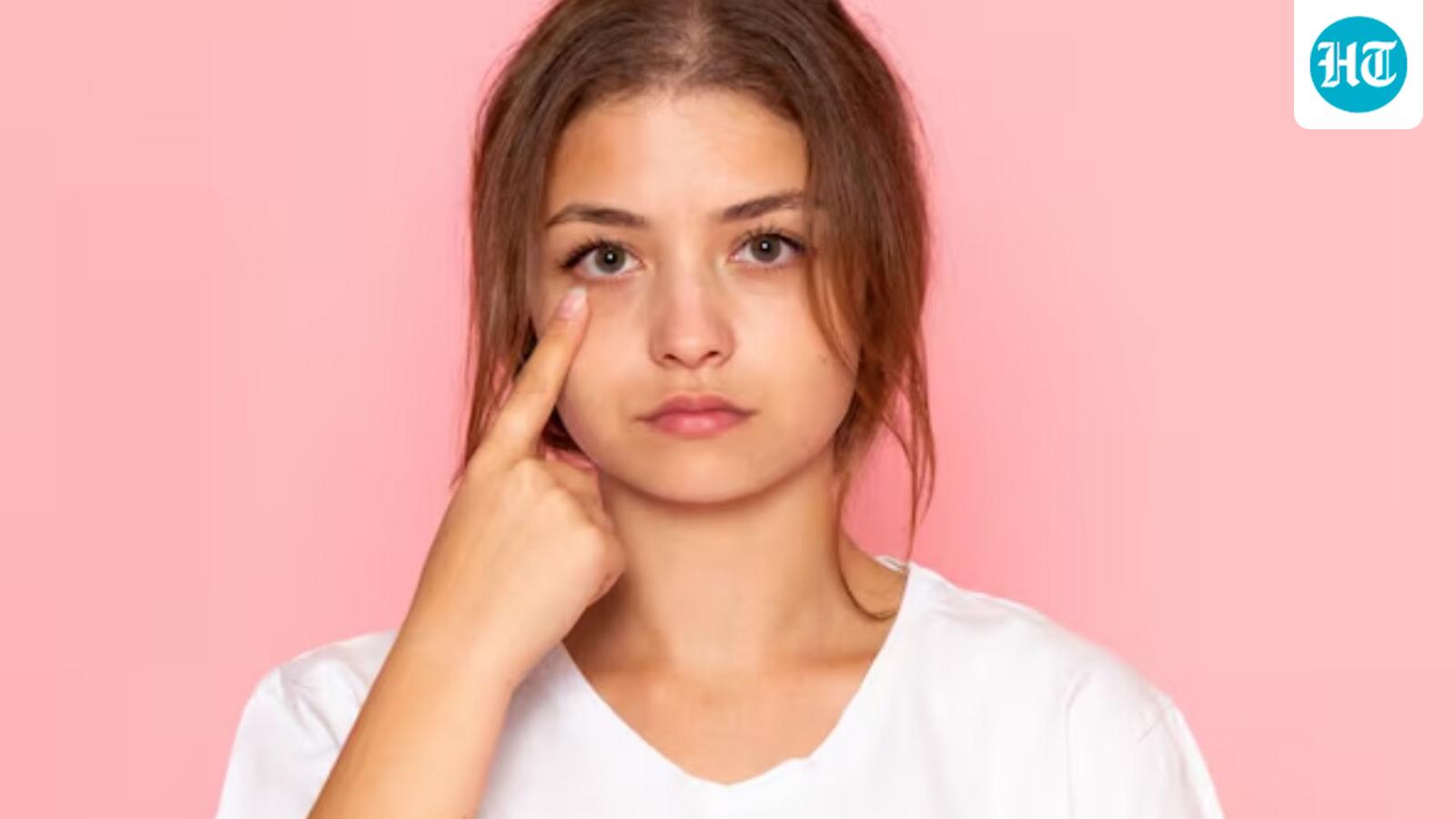
Magnesium deficiency, medically known as hypomagnesemia, often develops silently and goes undetected.One of its first and most common signs is eye twitching, a symptom that most people ignore or attribute to stress or fatigue.So how does magnesium treat eye twitching?
Magnesium plays a key role in calming nerve activity and relaxing muscles.When levels drop, the nerves can become overstimulated, leading to involuntary spasms of the eyelid muscles.Factors such as stress, lack of sleep, caffeine intake and dry eyes can make the condition worse.
According to the National Library of Medicine, long-term and severe magnesium deficiency has also been associated with nystagmus, a condition marked by involuntary eye movements.
Experts say that food should be the first method of correcting magnesium deficiency, and supplements are considered only when dietary intake is insufficient.Foods rich in magnesium include nuts, legumes, soy products, whole grains, and fruits such as bananas.
However, timing, quantity and personal health are all important. Nutritionist Vidhi Chawla, founder of the Aesthetic Nutrition Clinic, explains this further: "The magnesium pump is rarely announced out loud, but the body always gives signs. Recognizing these early signs and correcting them through careful diet and nutrition can prevent long-term problems and restore the overall balance."
The importance of magnesium
Magnesium is one of the most important elements your body needs because it supports biochemical and cellular processes.Magnesium acts as a cofactor in more than 300 enzymatic processes that help create and use cellular energy (ATP), produce proteins and nucleic acids (DNA/RNA), and regulate ion channels that control nerve signals and muscle function, according to PubMed Central.
In addition, according to nutritionists, magnesium supports:
- Normal muscle and nerve function
- Energy production and metabolism
- Regulation of blood pressure and blood sugar
- Bone health and vitamin D activation
- Stress response and sleep quality.
5 silent signs of magnesium deficiency
A nutritionist shares a few signs you shouldn't ignore that indicate a magnesium deficiency;
Eye twitching or muscle spasms
This is the first symptom that indicates magnesium deficiency in the body.Conversely, magnesium relaxes muscles;Lower doses may cause involuntary twitching, especially around the eyes or calves.
Frequent headaches and migraines
The low magnesium content can affect the function of blood vessels and the balance of neurotransmitters, causing tension headaches or migraines.
Insomnia or restlessness
Magnesium supports GABA, a calming neurotransmitter.Lack of magnesium makes it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep.
Magnesium deficiency causes irritability, mood changes, or increased sensitivity to stress, which may be due to insufficient magnesium intake.
How much magnesium do I need?
According to the National Institutes of Health, magnesium needs vary by age and gender.Adult men generally need 400-420 mg per day, while adult women need 310-320 mg.Pregnant women need about 350-360 mg per day, and nursing women need 310-320 mg per day.
Note: Dietitian advises to be cautious about magnesium intake and seek medical advice.
Who is at risk?
Dietitians say that magnesium deficiency is more common than assumed, and especially among;
- People with high levels of stress.
- Those who eat a highly processed diet.
- Individuals with diabetes or insulin resistance.
- People with digestive problems (IBS, dyspepsia).
- Excessive consumption of caffeine or alcohol.
- Athletes and people who sweat a lot.
- Pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds
- Almonds, almonds, pistachio
- Spinach, Amaranth, Fenugreek
- Cereals (brown rice, millet, oats)
Dark chocolate (70%)
- Bananas and avocados
- Consistent food intake is the safest and most sustainable approach, say nutritionists.
Dietitians say that if complaints persist despite a balanced diet, supplementation may be considered under professional supervision.
- Recommended types: Magnesium glycinate or magnesium citrate (better absorbed and gentler on the intestines)
- The time to drink: in the evening or before going to sleep, especially if it is a concern of sleep or muscles.
Caution: Taking too many supplements can cause diarrhea, low blood pressure, or drug reactions.Avoid self-medication in high doses.
(Note to readers: This article is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always seek the advice of your doctor if you have questions about a medical condition.)
Read your daily dose of the latest fashion lifestyle news, Taylor Swift, health, festivals, travel, relationships, recipes and more on the Hindustan Times website and app.
Catch your daily levels of fashion, Taylor Swift, health, festivals, travel, contacts, recipes and the latest lifestyle news on the Hindustan Times website and app.